
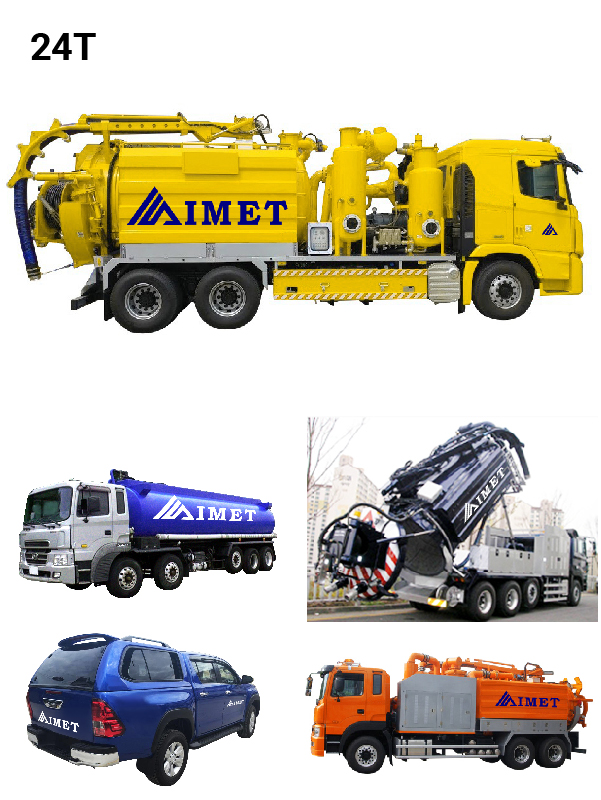
Sewage Treatment and Maintenance
IMET manage the drainage and inspection by using hi-technology machine which can provide the easiest and fastest way of cleaning pipelines. Cleaning and inspection can be done simultaneously, which can save time and money. The timetable for cleaning and inspection depends on the location and status of pipeline.
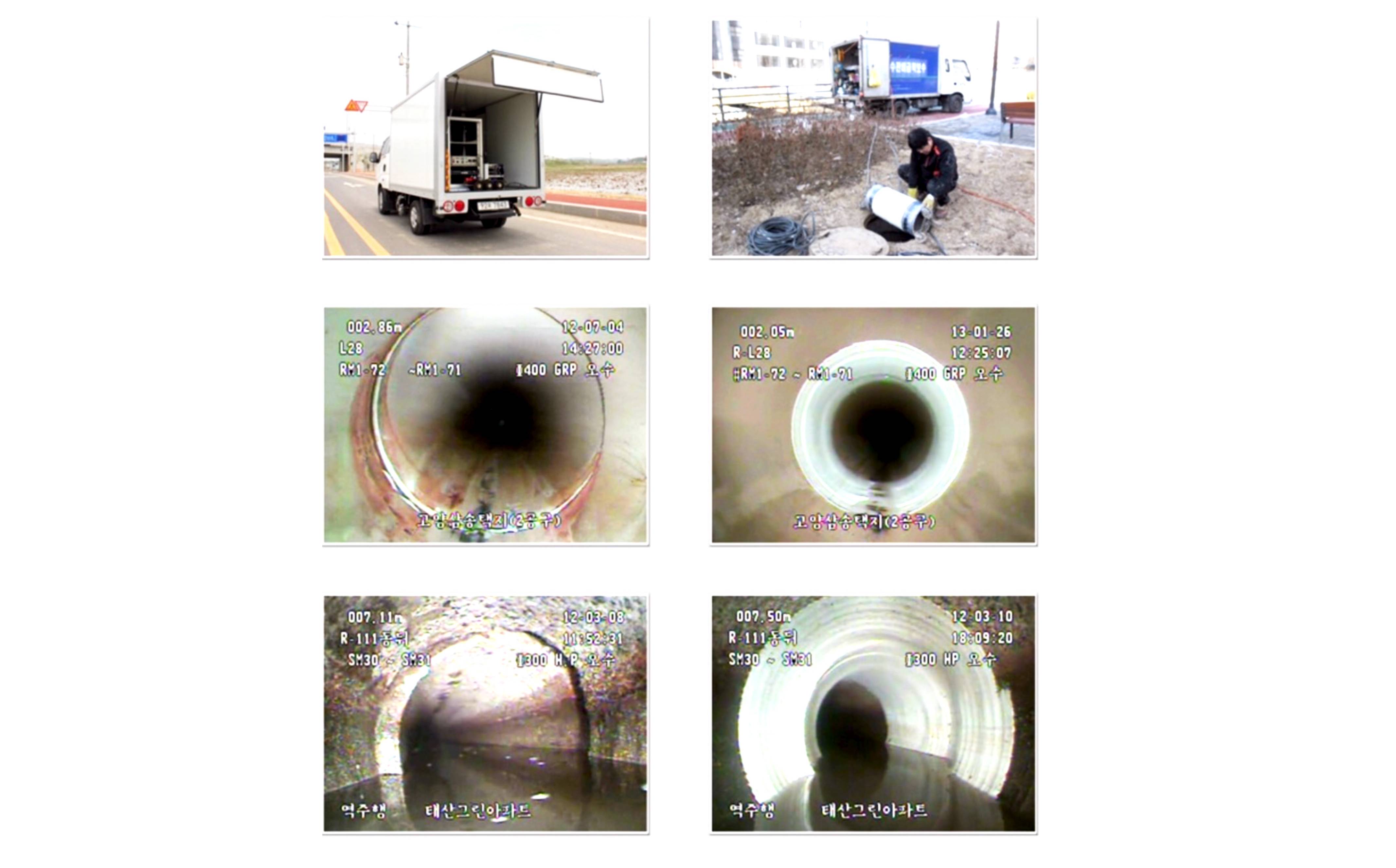
Pipeline inspection is the process of checking on the conditions of pipelines using IMET’s high-tech inspection service car in collaboration with the high-tech robot. Result of inspection will be provided when the operation is done or as needed by the client.
It is a operation control vehicle that monitors all the inspection inside the drainage pipelines such as condition of drainage pipelines.. It is also use for Water and Smoking Testing that locates illegal pipelines or if the pipelines place correctly based on the blueprint/record of the Government Engineering Department.
These two inspection machines are working together to provide accurate report during and after the operation.
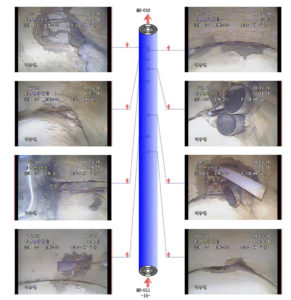
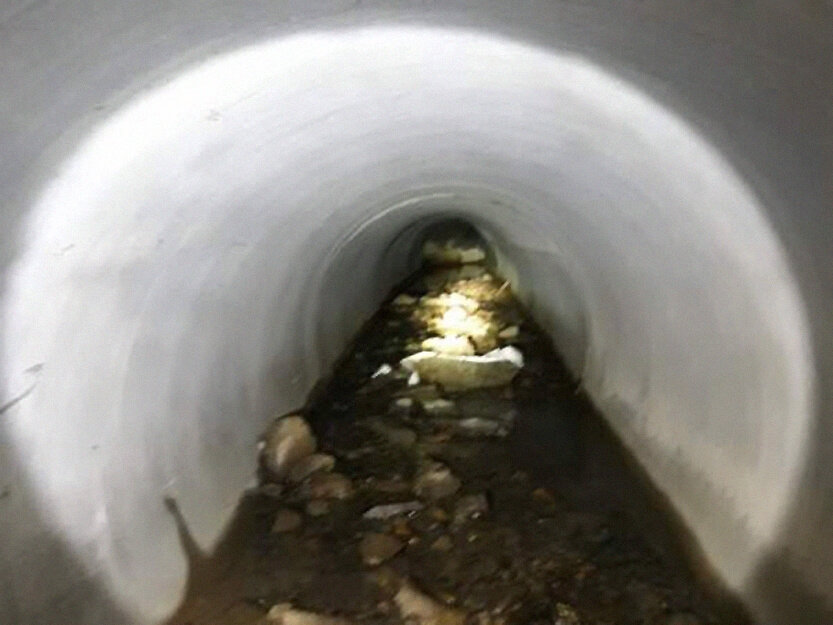
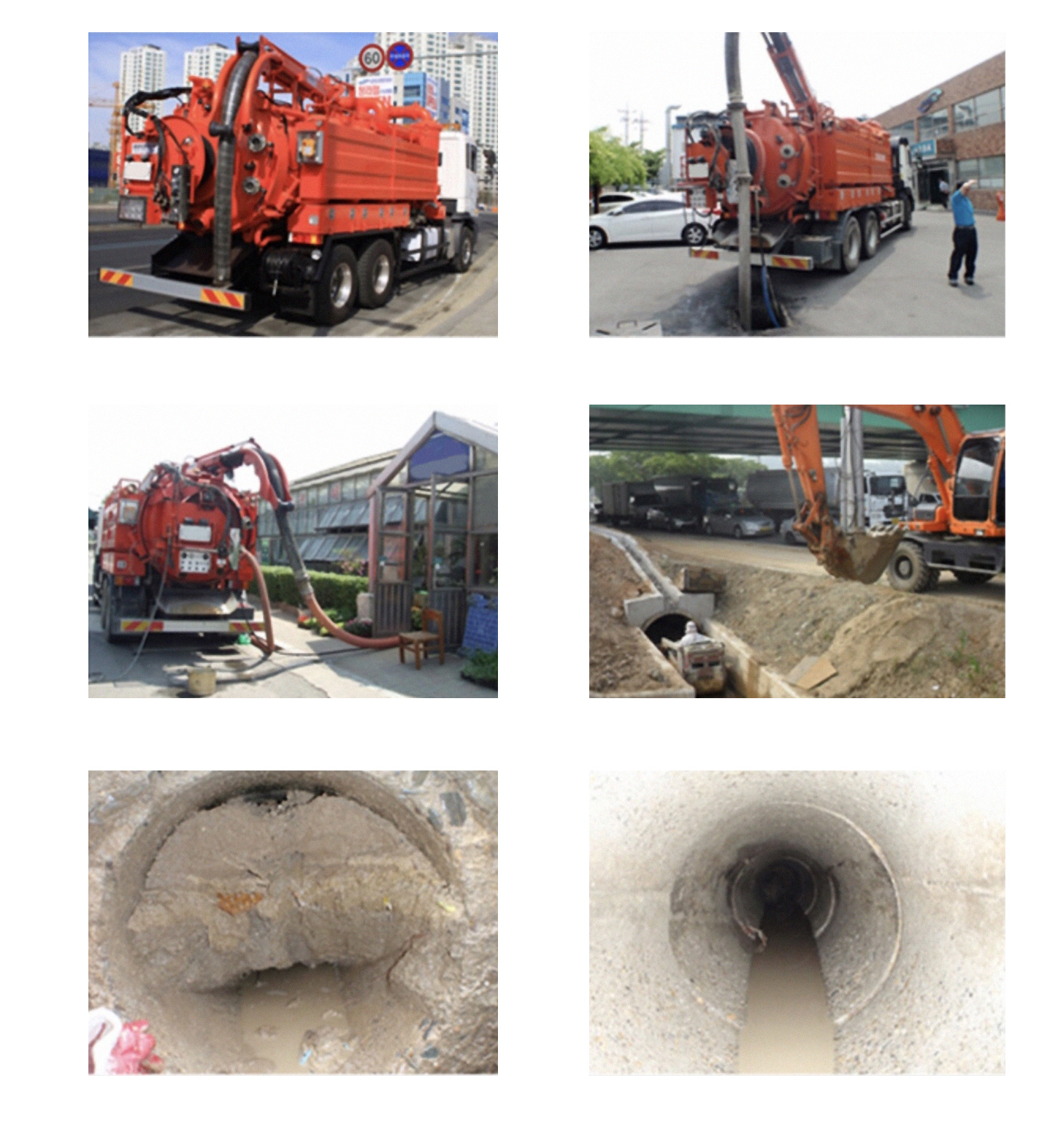
Illustration of Illegal Pipes and Joint Damage inside Storming Pipes
As the standard of water quality for discharging after sewage/waste water processing became more strict. Existing processing methods could not meet the quality of the water to the fortified standard. Thus, IMET using the high-tech machines we could meet the required quality of water and may decrease the labor time and cost of maintaining pipelines of the company





During the operation IMET is using high pressure Jet-Cleaning equipments and high vacuum suction vehicle. All the wastes and sludges(sand, pebbles and other matter) are pushed by high pressure water that is discharged from high pressure jet-cleaning equipment then these wastes are sucked into suction hose of vacuum car that is attached to manhole, making dredging completely.
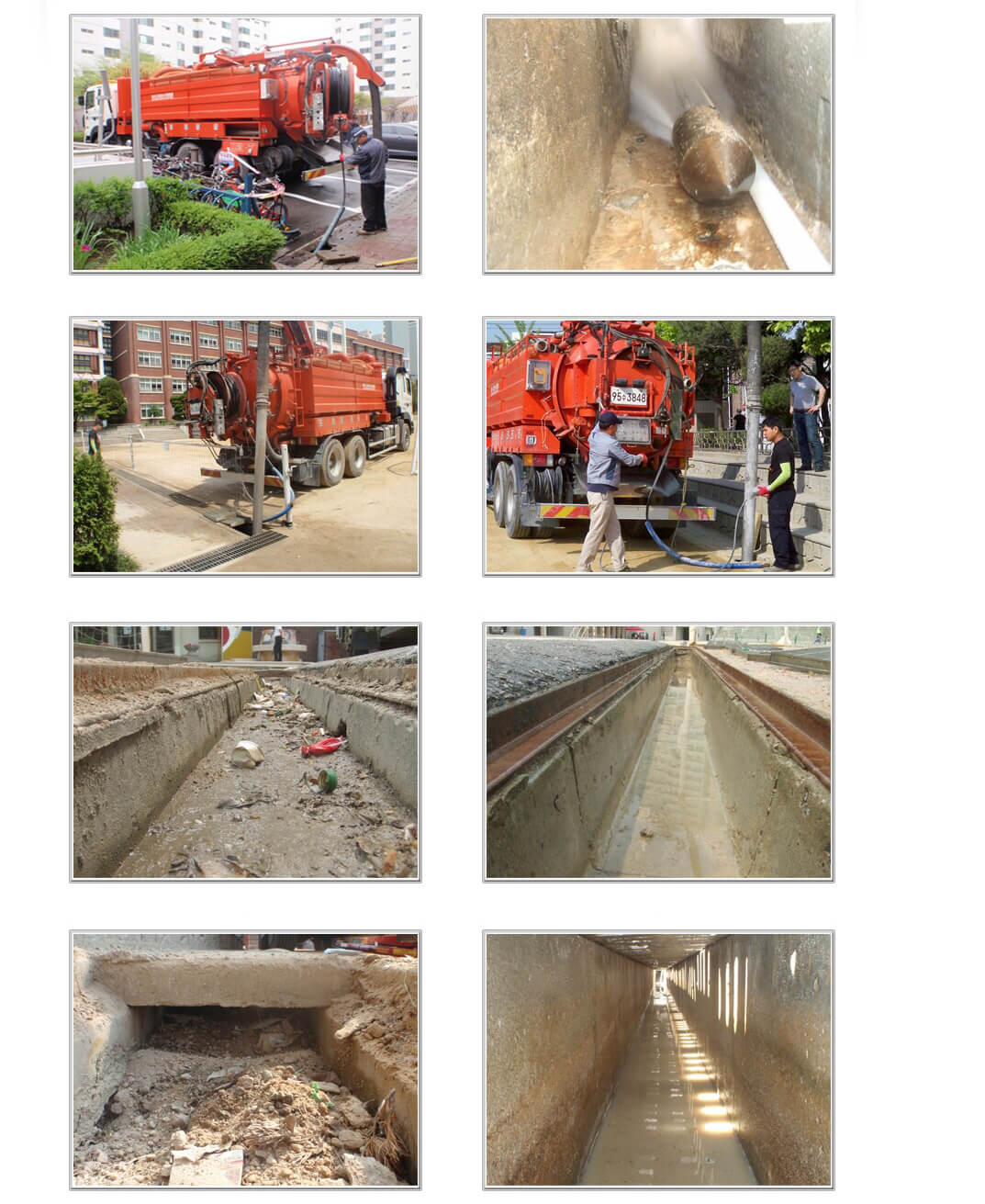
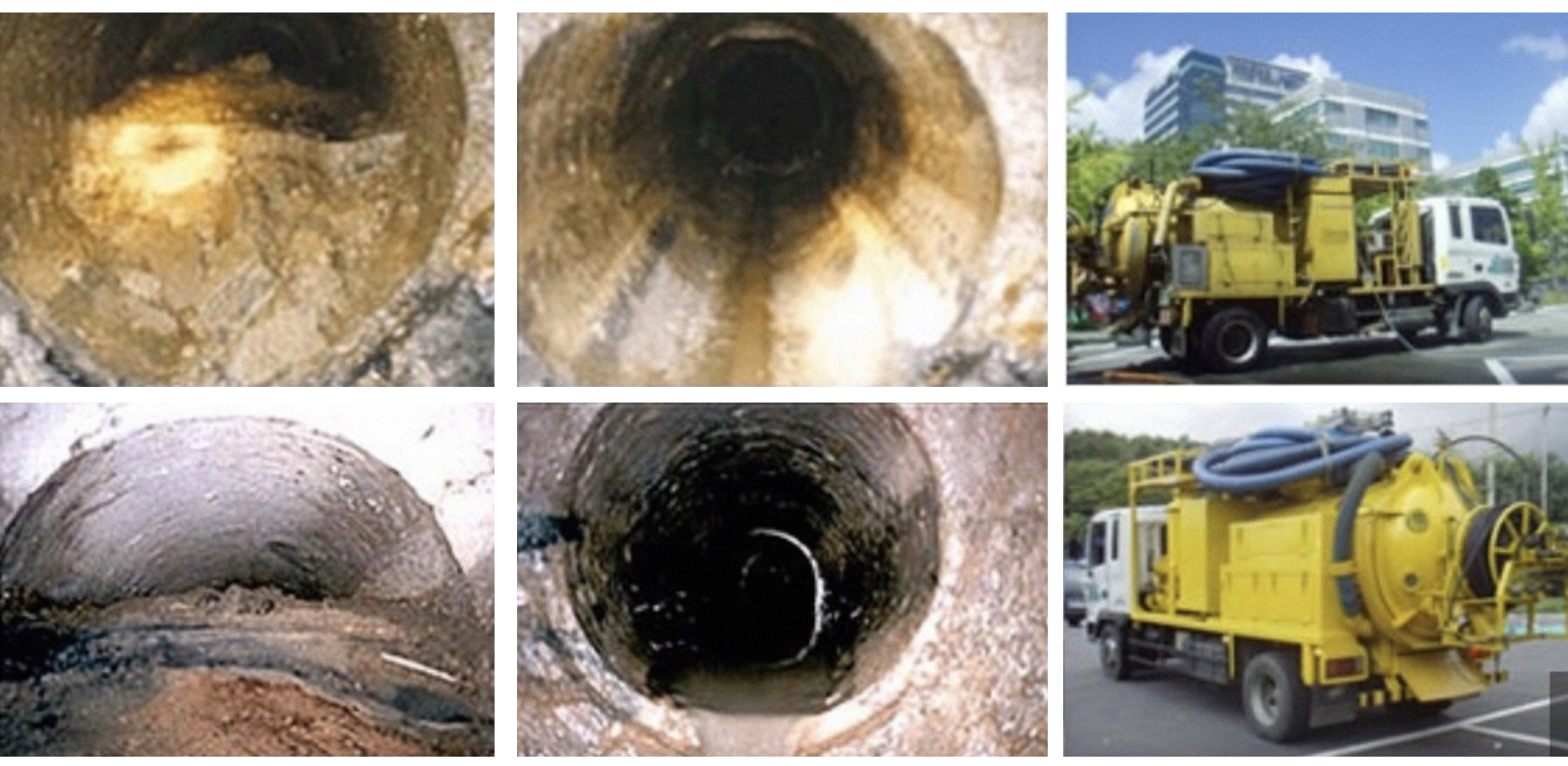








 Smoke demonstration
Smoke demonstration



Supplements shortcomings of the existing watertight test and effectively inspects drainage pipe leak. It is fast, accurate and economical way to check piping and construction after construction of new or existing buildings and repair. This simple and easy test can save inspection time and the test is available regardless of the ground water level. It accurately identifies the location of leak as well as performs partial pneumatic pressure test for possible leak area.
Test procedure
 Pneumatic pressure test inspection
Pneumatic pressure test inspection

1. Pneumatic pressure test is to inspect the span of conduit and watertightness of the connections through air pressure. Manholes are excluded from the test due to possible damage.
2. Conduit test, due to the difference in nature of water and air even at the same pressure, can view pneumatic pressure test and hydraulic test results equally and pneumatic pressure test can be considerably affected by the conduit air gap, water content and pipe thickness.
3. Even for conduit facilities whose watertightness is confirmed, certain amount of air loss is unavoidable when applying pneumatic pressure. Therefore when performing low pressure air test on sewage conduit, air loss according to pipe type, pipe damage part and connection defect should be divided.
4. Pneumatic pressure test methods include constant pressure method and time pressure method; and time pressure method applies to sewage conduit watertight test.
5. For pneumatic test for newly constructed conduit, LC and LD methods are used according to pipe diameter, pressure(Po), acceptable decompression amount(△Po); for the existing conduit, the methods are divided according to the pipe diameter. However consult with the buyer regarding application before performing test.
1) The first initial pressurization should be 10% more than that of each inspected pressure during the preliminary pressurizing time. (e.g. Initial pressurization of LB: 5*1.1=5.5kPa)
2) After preliminary pressurization, it is actual measuring stage and decompression amount(△P) measured continuously during the measuring time(t) according to each test method is compared to the acceptable decompression amount(△Po) to determine PASS or FAIL.
3) It is considered PASS if the measured decompression amount(△P) is smaller than the acceptable decompression amount(△Po).
4) Test standards, inspected pressure(Po), acceptable decompression amount(△Po) and measuring time(t) are the same as for the test acceptable amount according to pipe diameter
6. For larger conduits(over 1000mm), test mainly on the connections and prepare the test report.
7. When applying compressed air test methods, please be aware of the followings.
1) Conduit’s wetting state, pipe type and pipe diameter should be considered when the inspection method is discussed with the buyer.
2) Ground water plug should be kept confidential for construction. In the testing area, the air pressure should not be dropped to the level of atmospheric pressure.
3) For safety, access to the manhole should be restricted during the test and the test instrument should have decompression device.
Sewage conduit is installed underground and may cause lack of attention due to site renovation, etc. Therefore, perfect construction is required to prevent weak construction, ground water pollution and water pollution in the public basin.
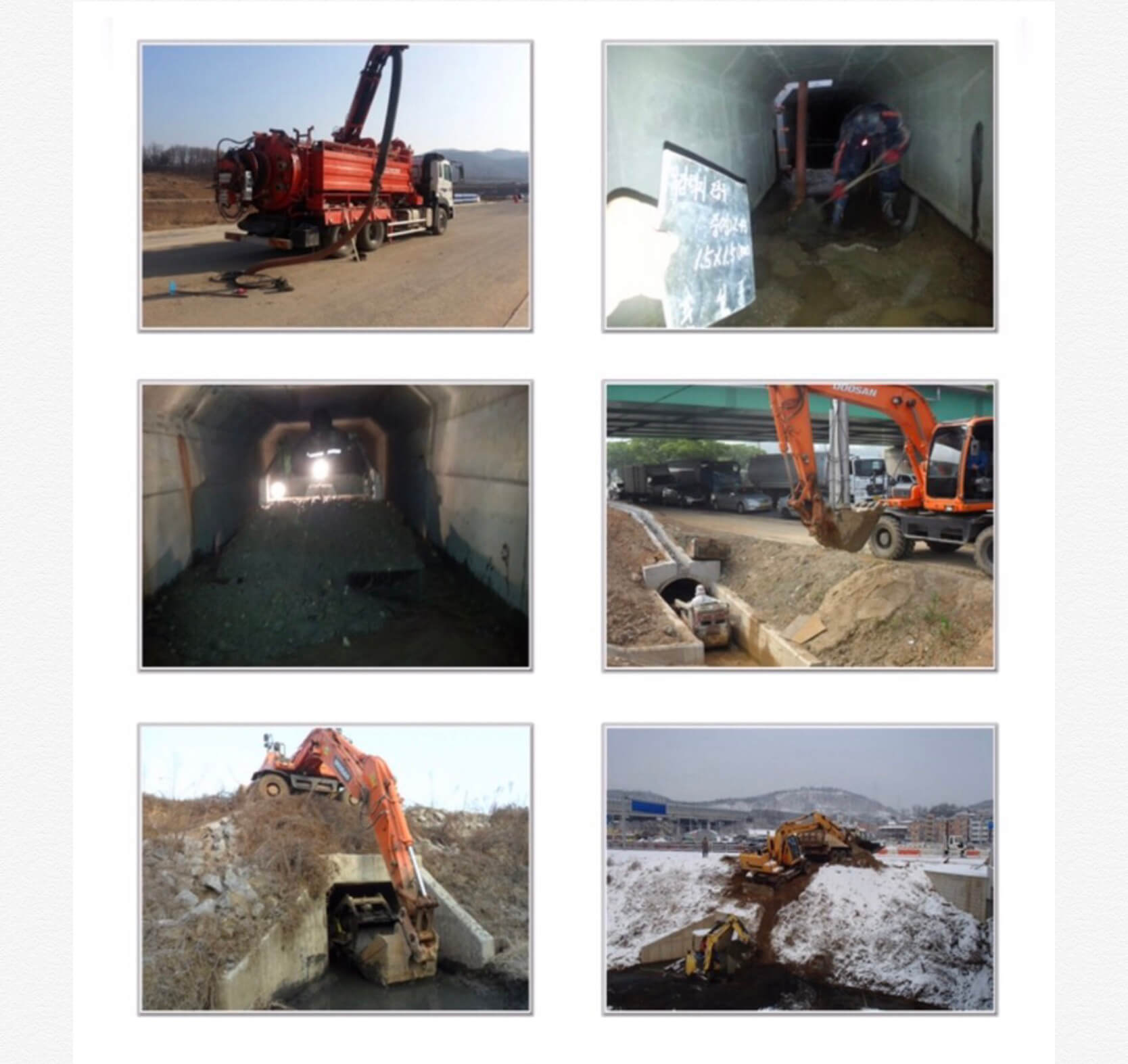
Water test procedure
1 test area should be between manholes. Clean the inside of the conduit before testing, keep the ground water level lower than the bottom of the conduit. Leak test procedure is as follows:
Step 1 Plug a stopper that can stand against the total pressure at the lower end of the conduit or if needed, at the underground pipe.
Step 2 Install similar stopper or supporting wood at the upper end and make sure to keep a hose or a vertical pipe stand.
Step 3 Fill water in to avoid generating bubbles.
Step 4 Fill water in the vertical test tube up to the required level.
Step 5 Leave it at least for 30 min. until the preventive conduit line for submerged lower area is saturated.
Step 6 Fill water in to keep the head at 1.0m and measure water amount required to maintain the head of the vertical test tube at 1.0m, for over 10 min.
 Water test demonstration
Water test demonstration


